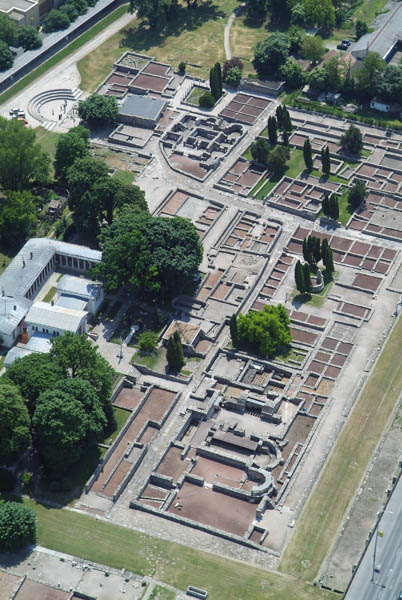
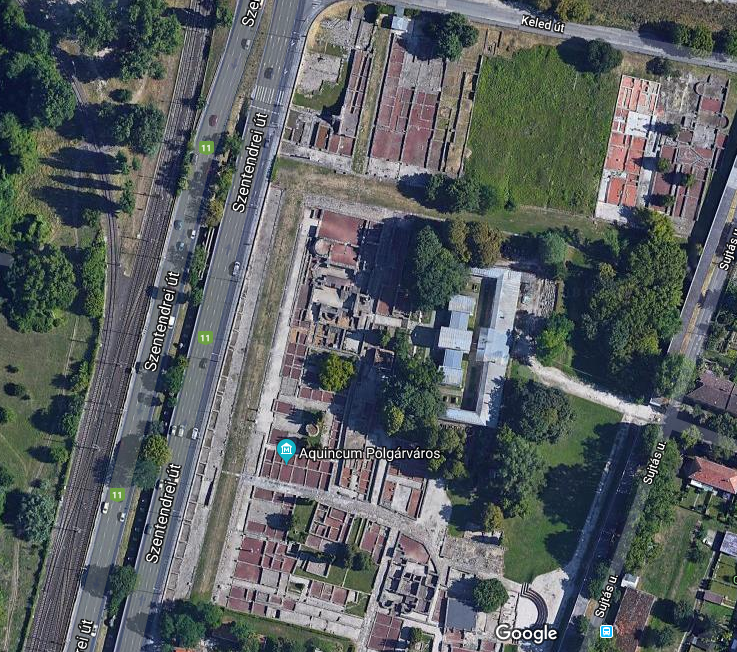
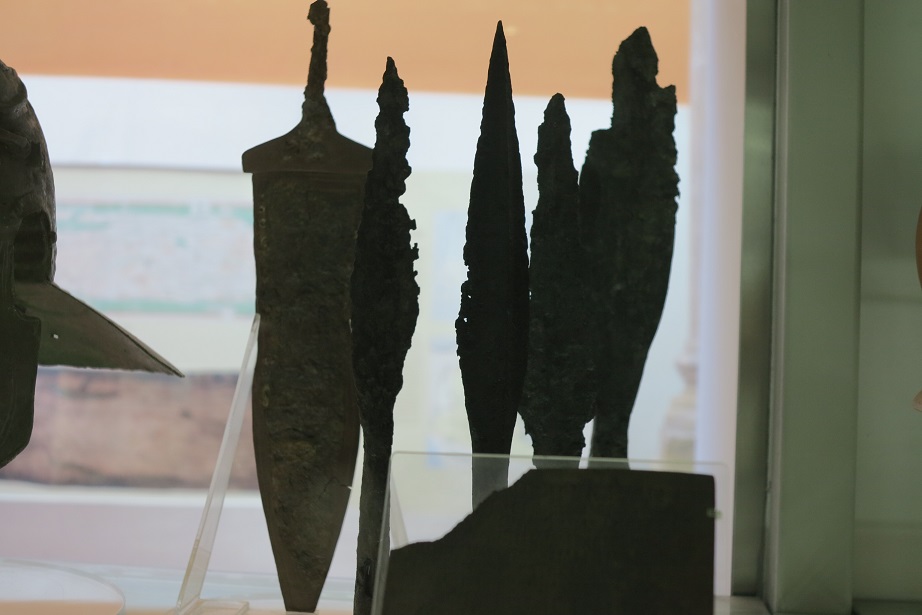
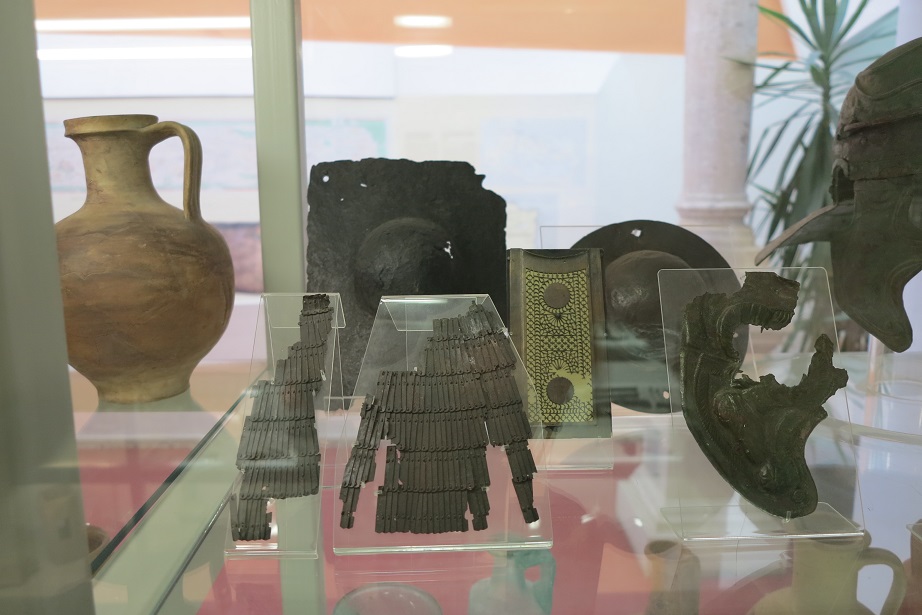
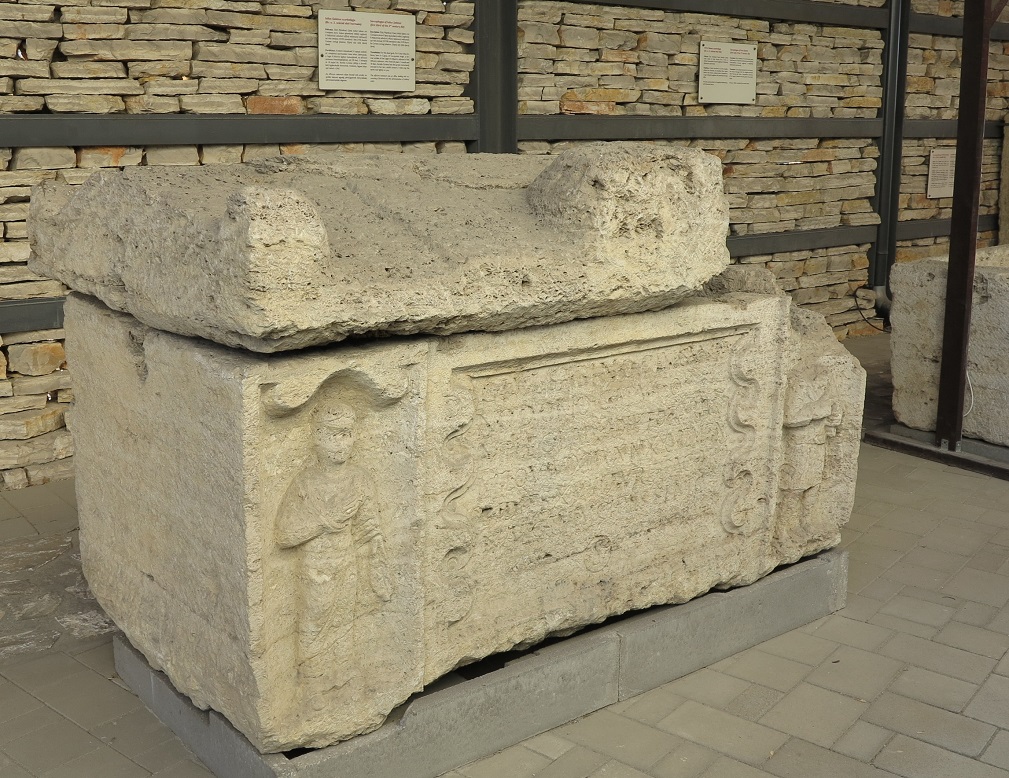
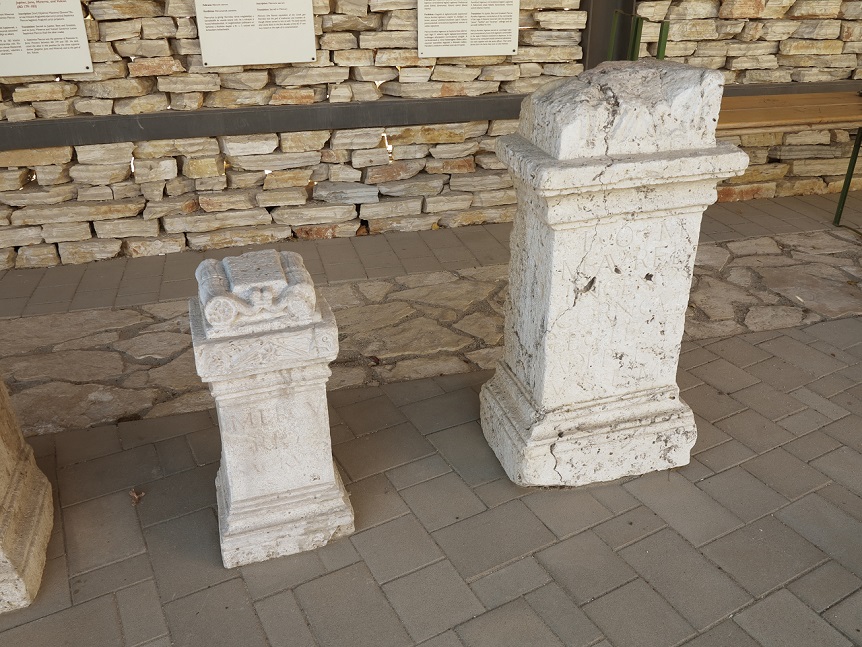
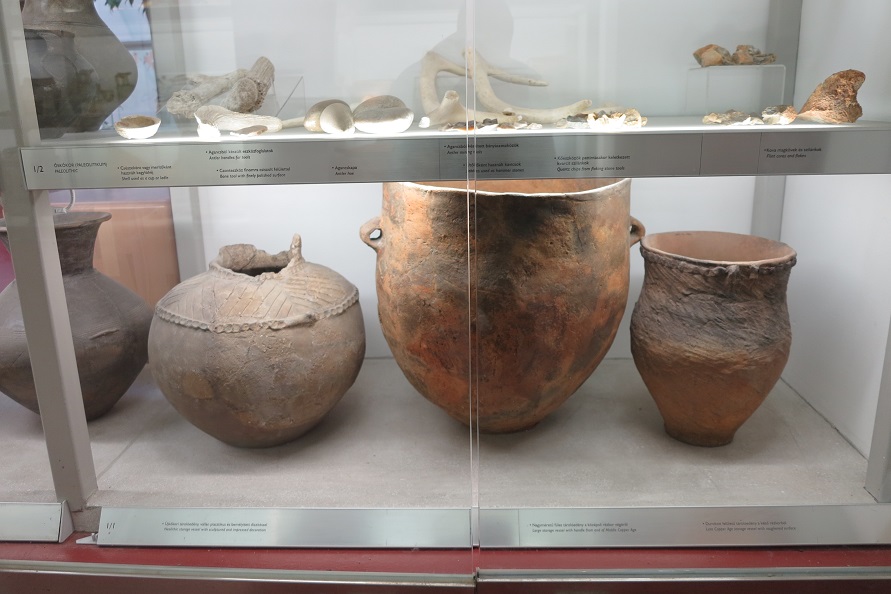
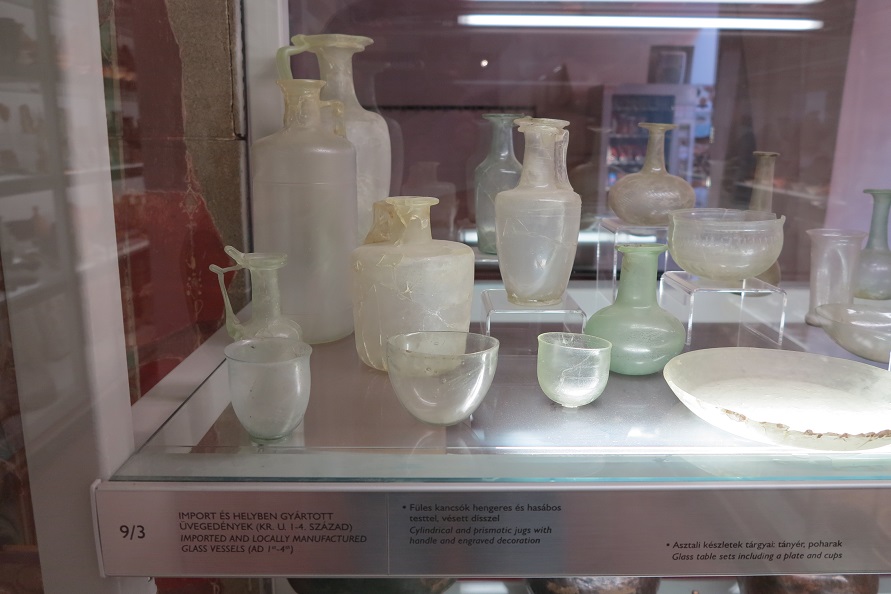
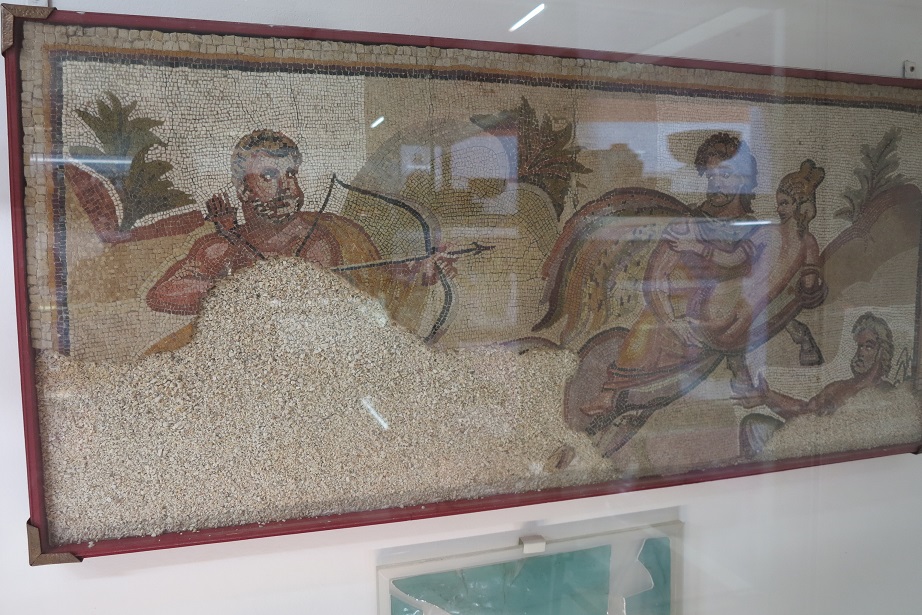
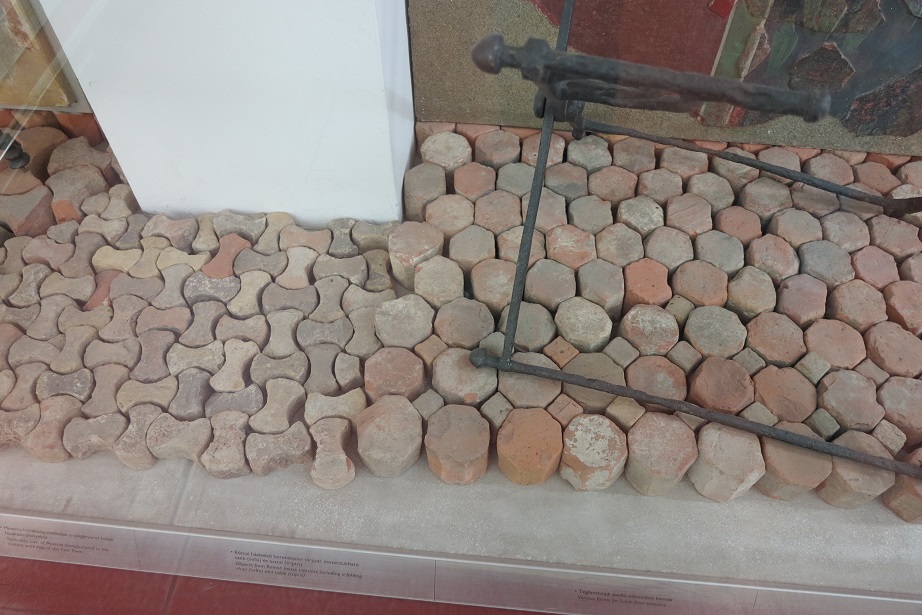
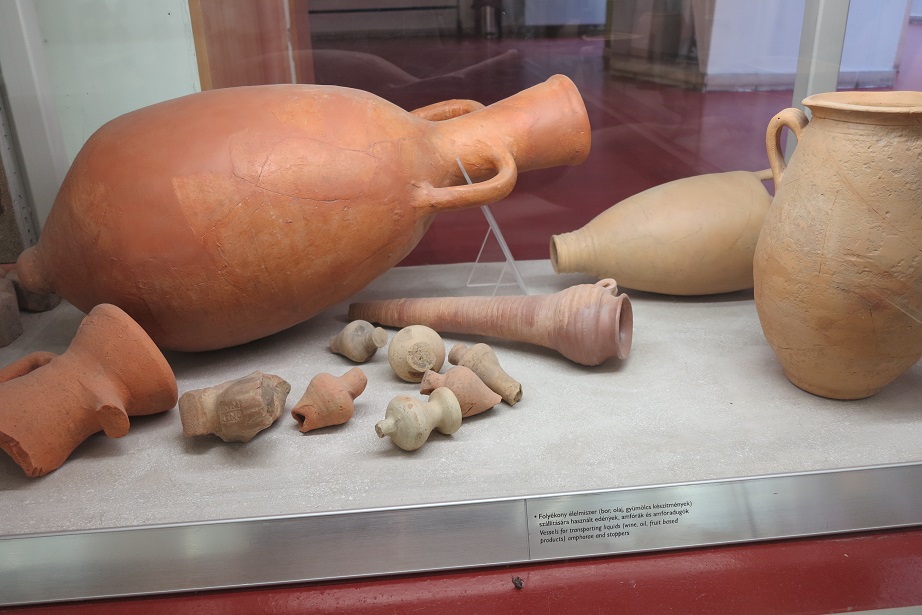
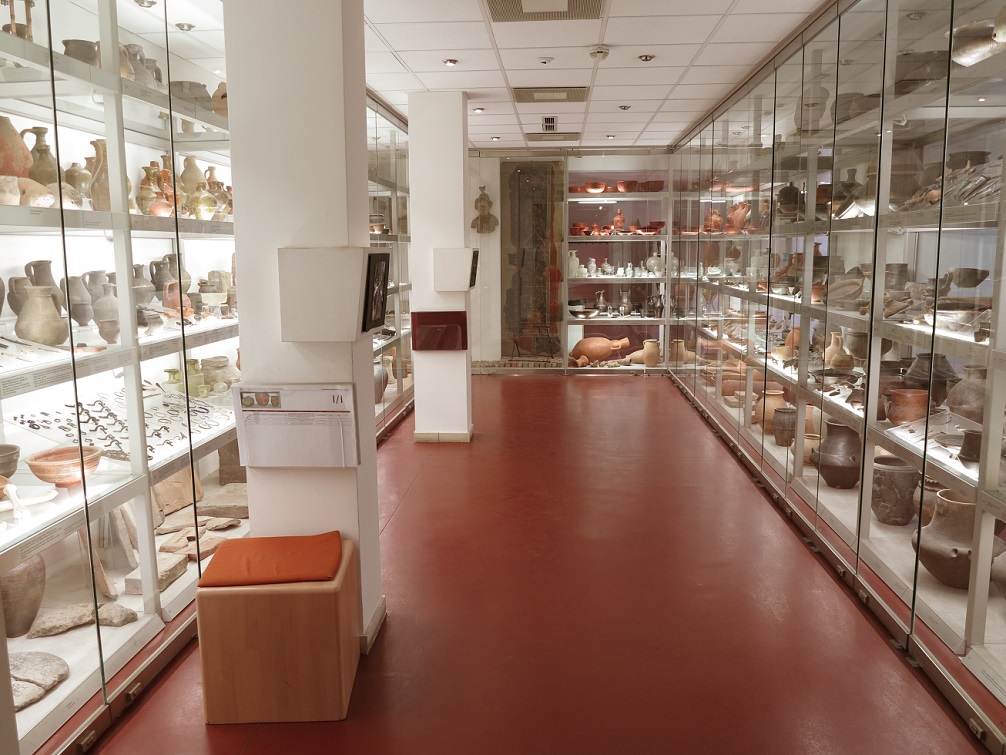
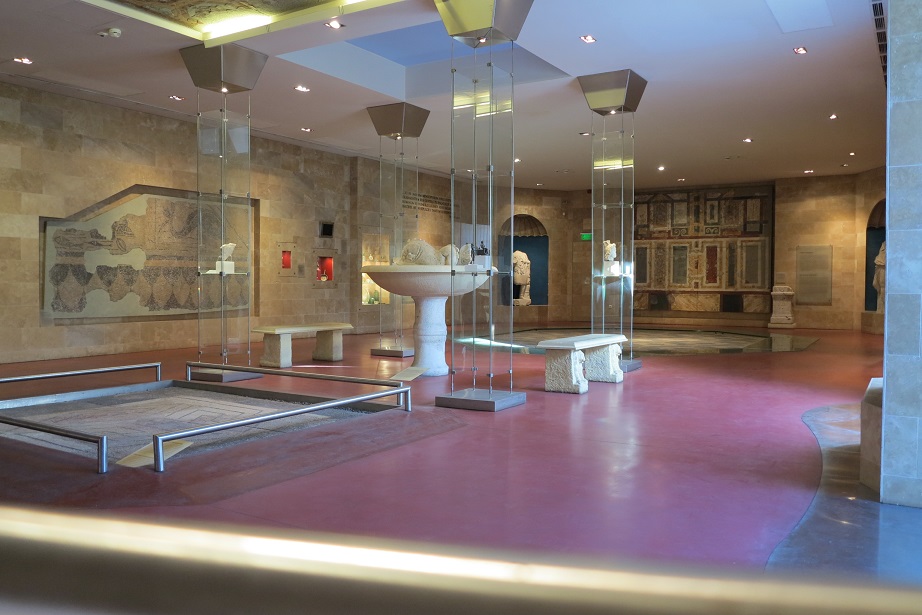
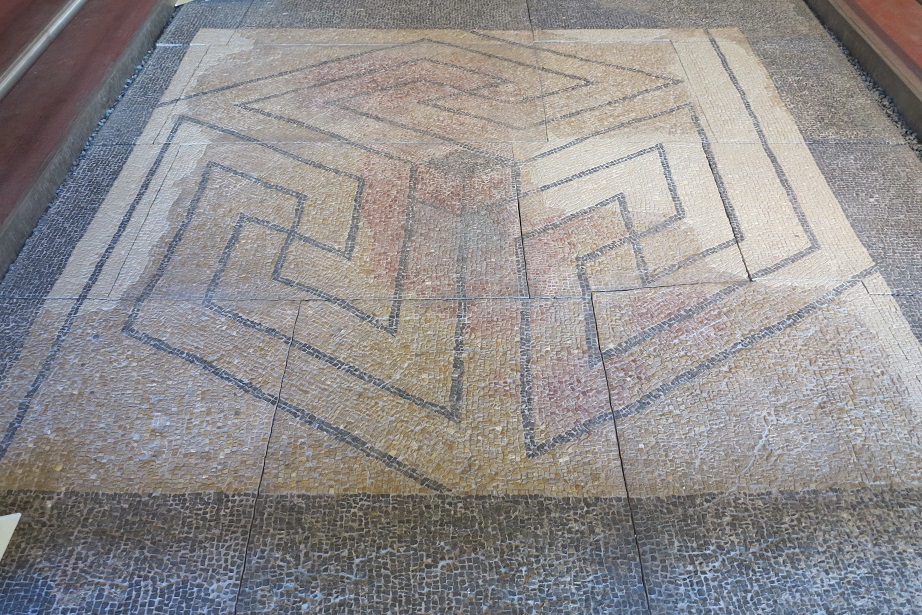
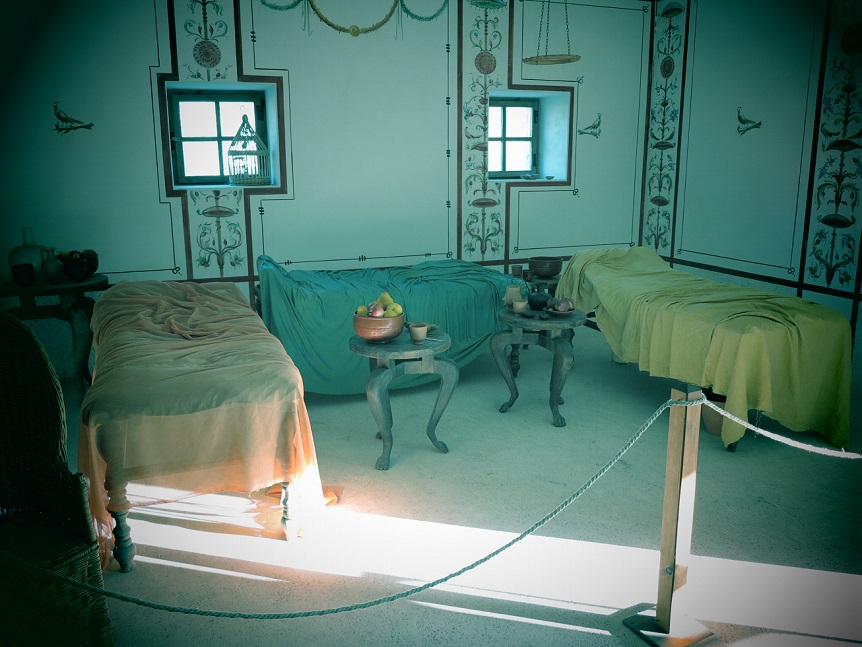
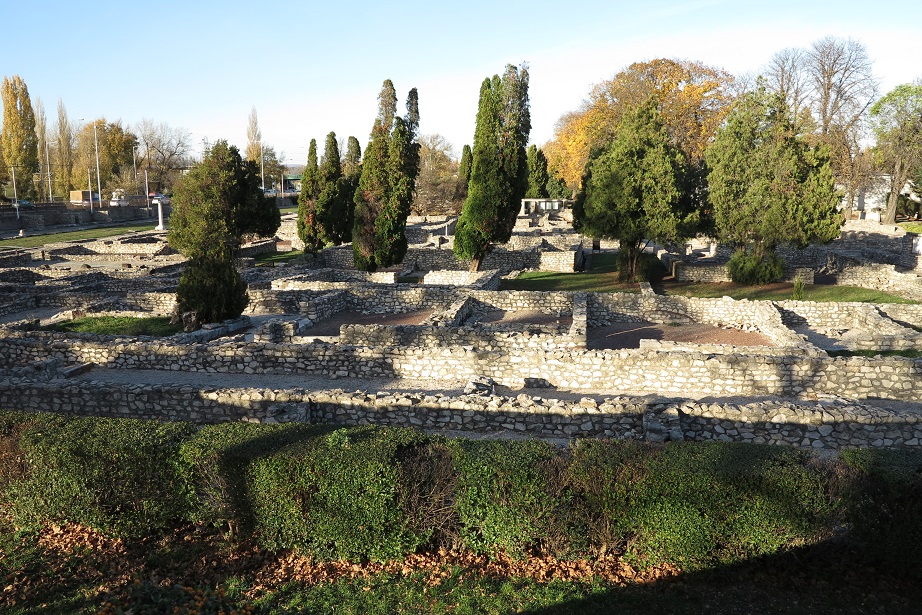
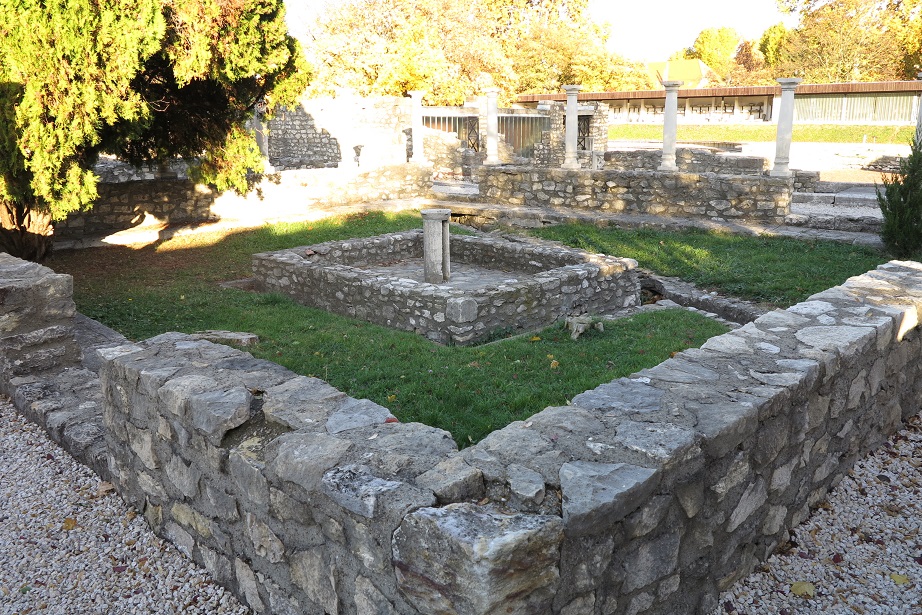
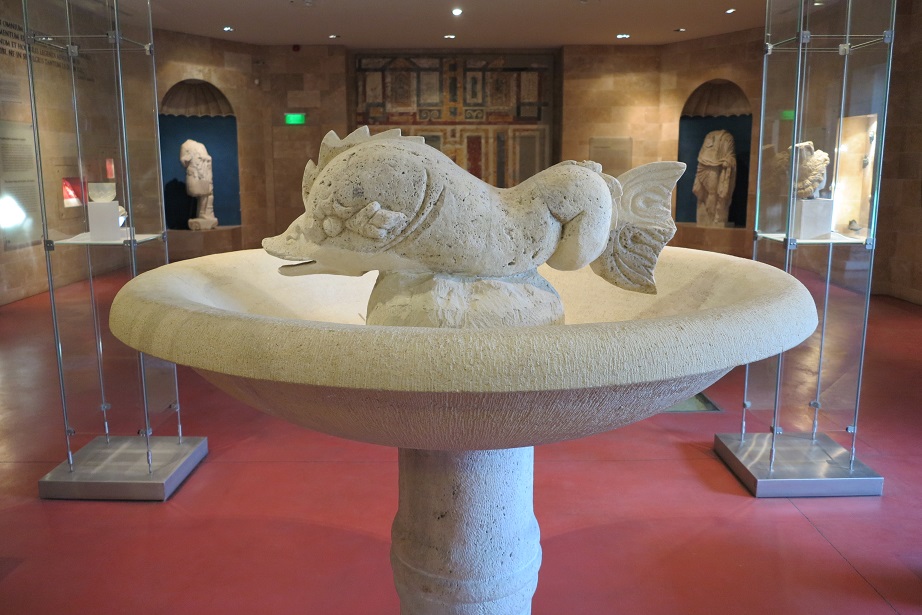
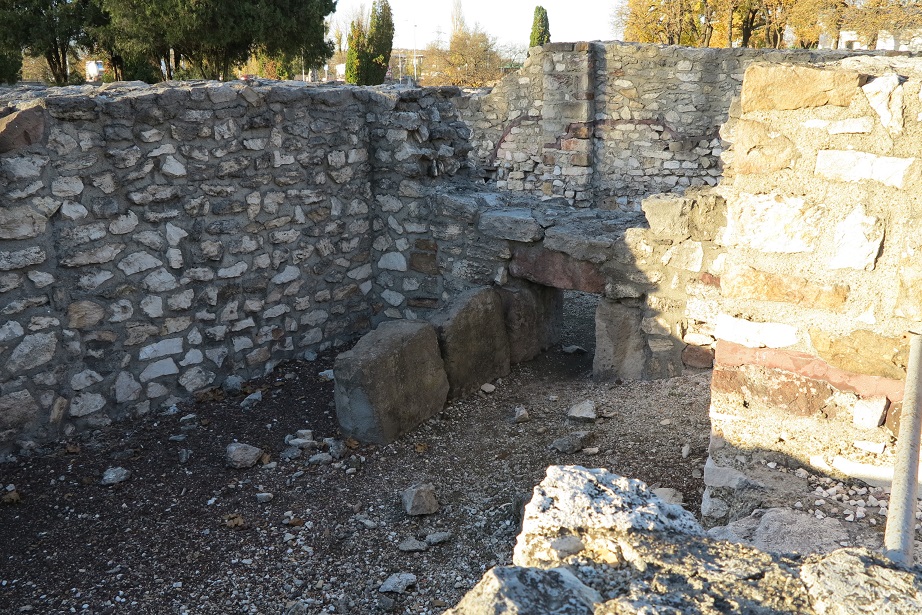
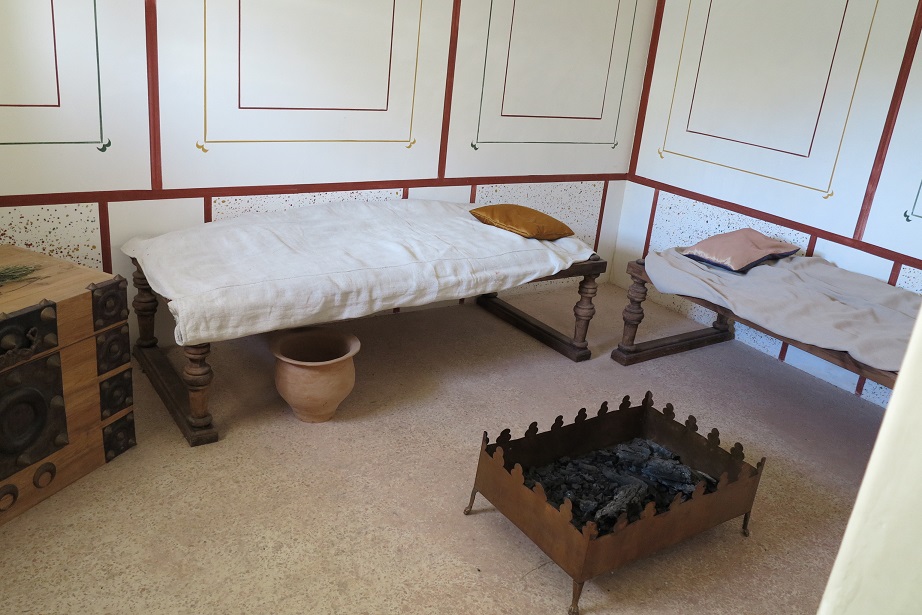
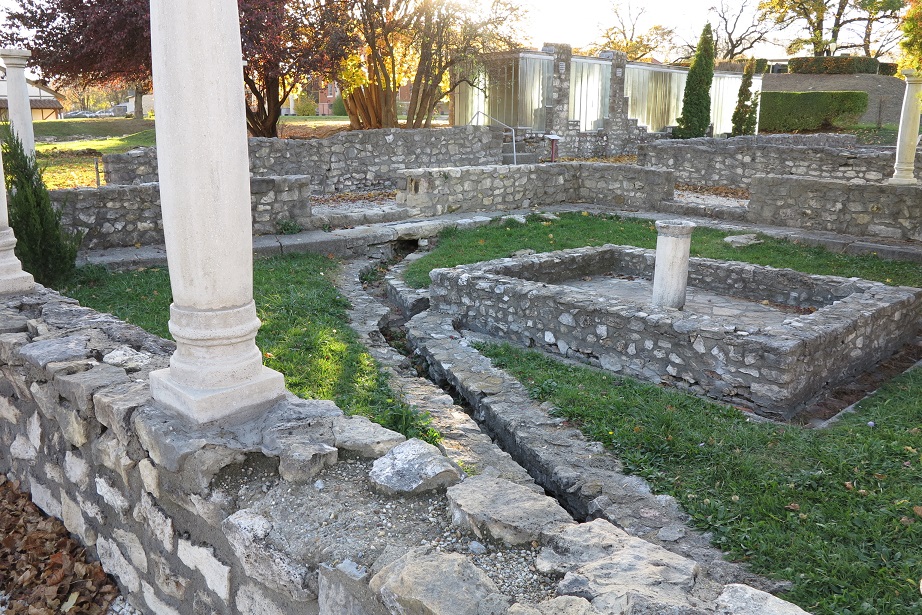
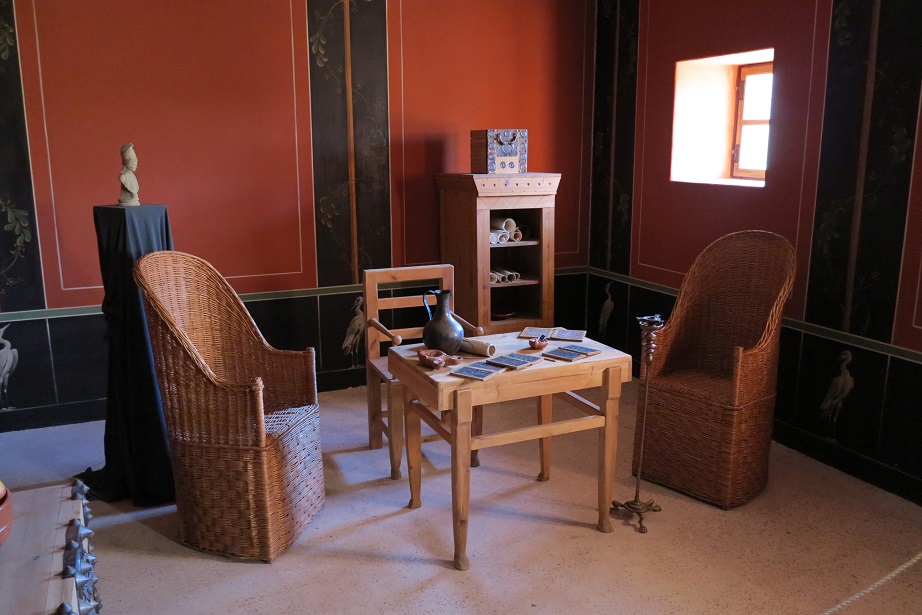
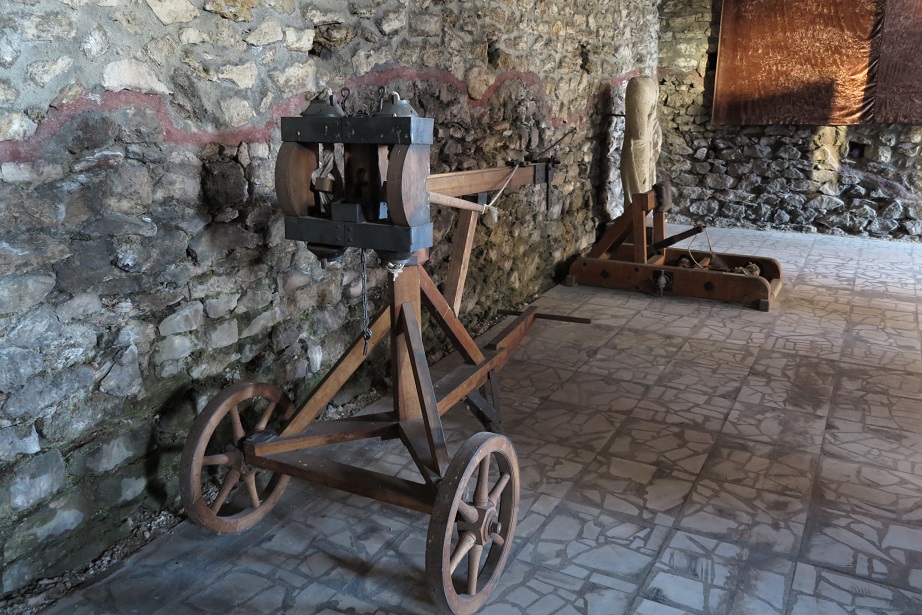
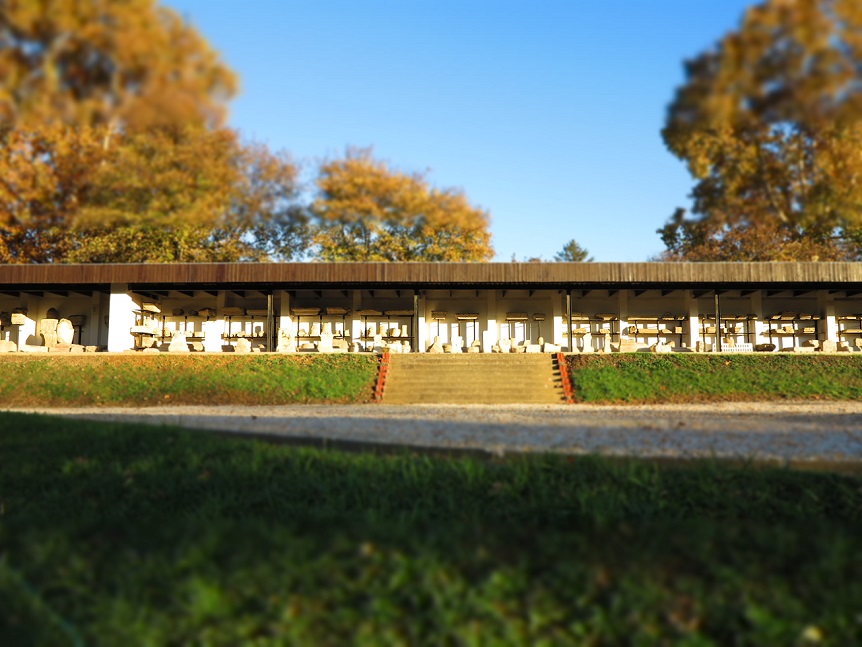
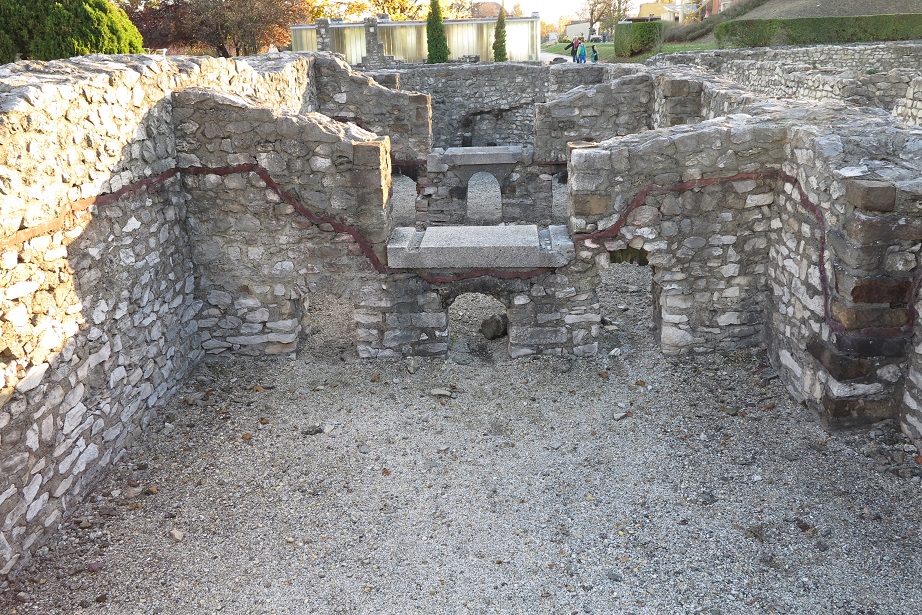
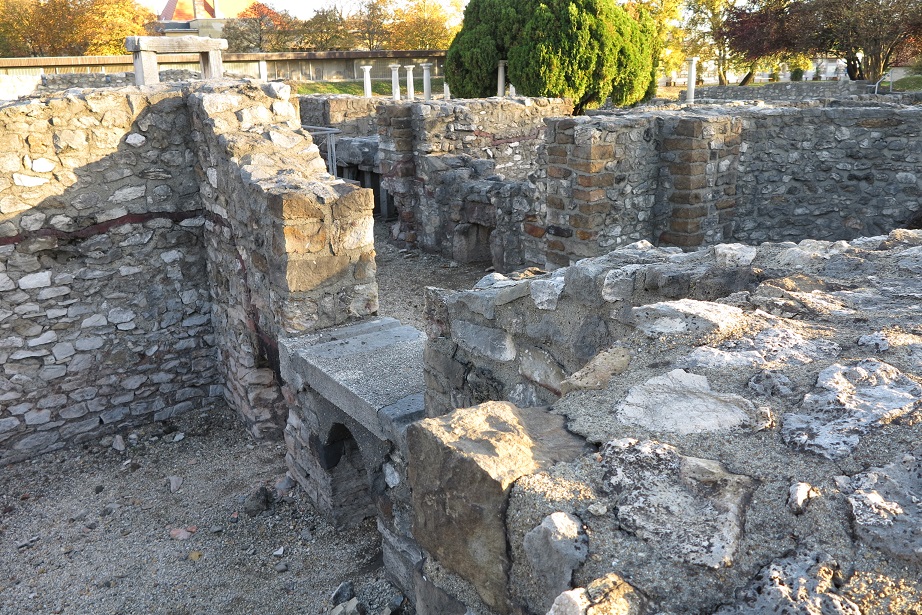
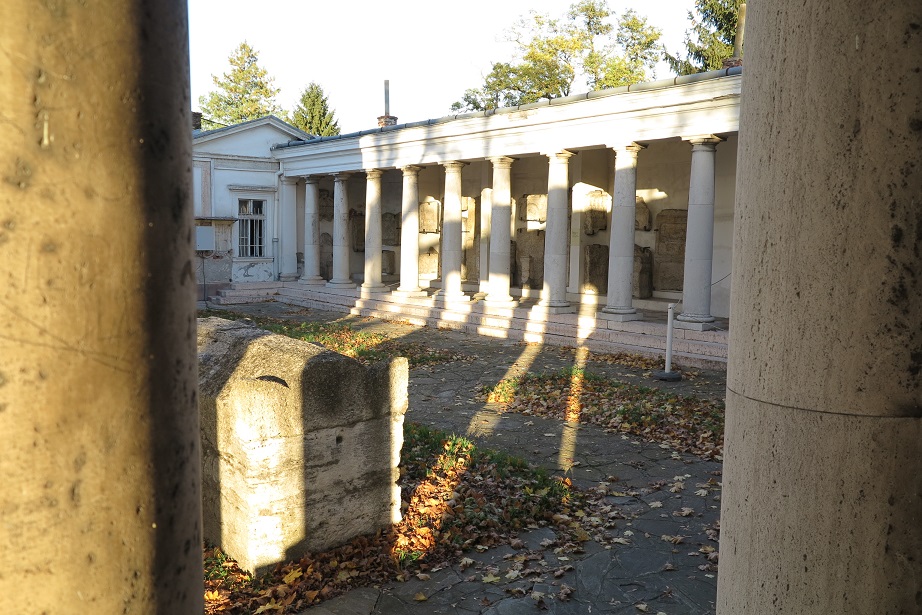
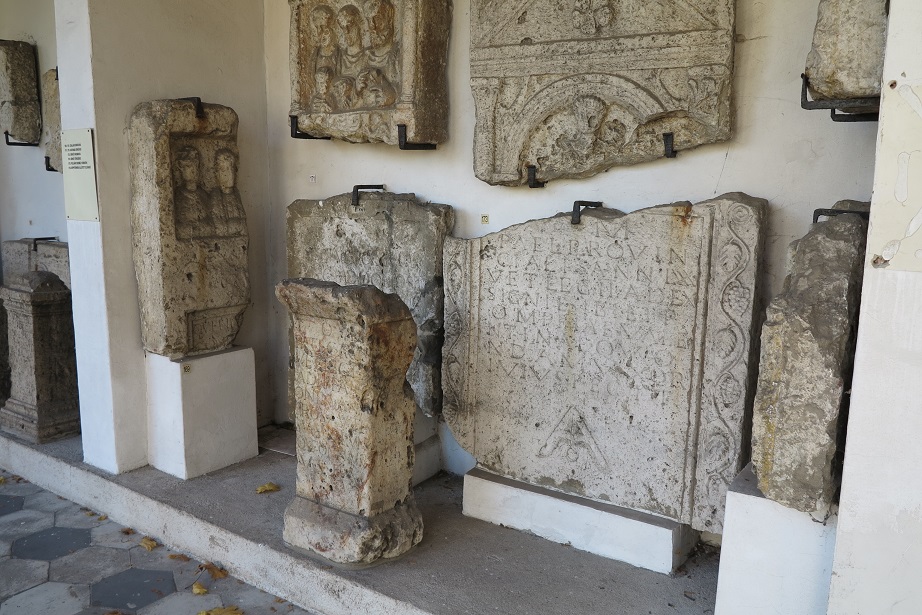
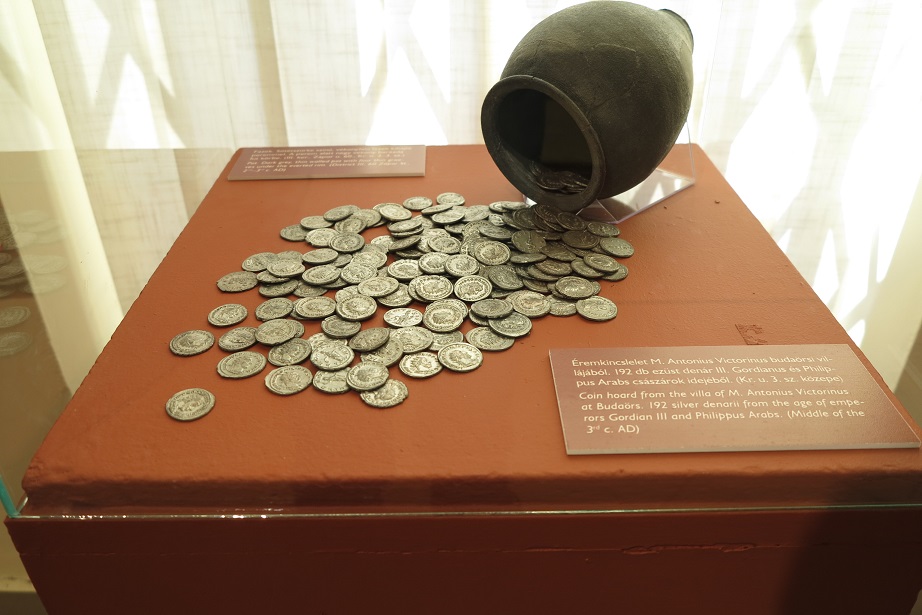
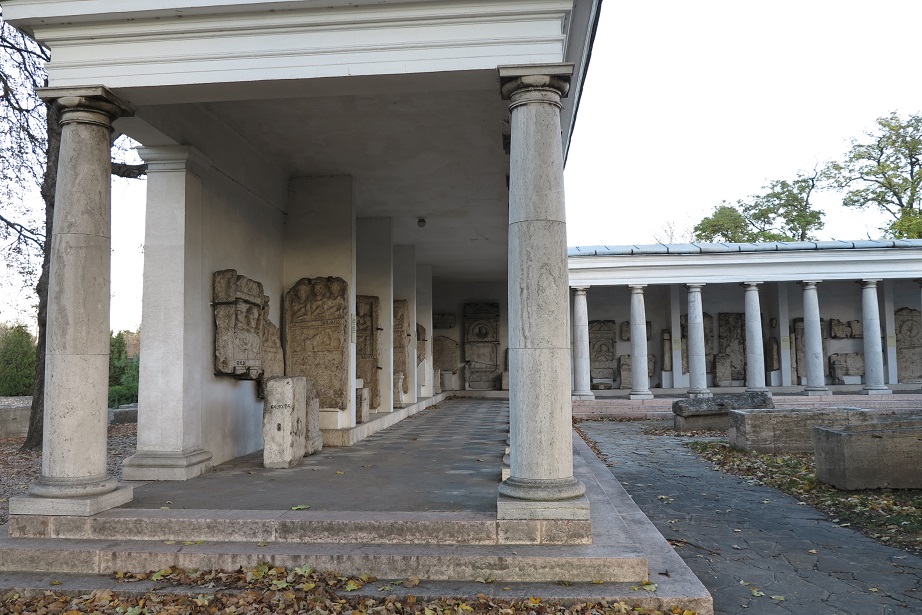
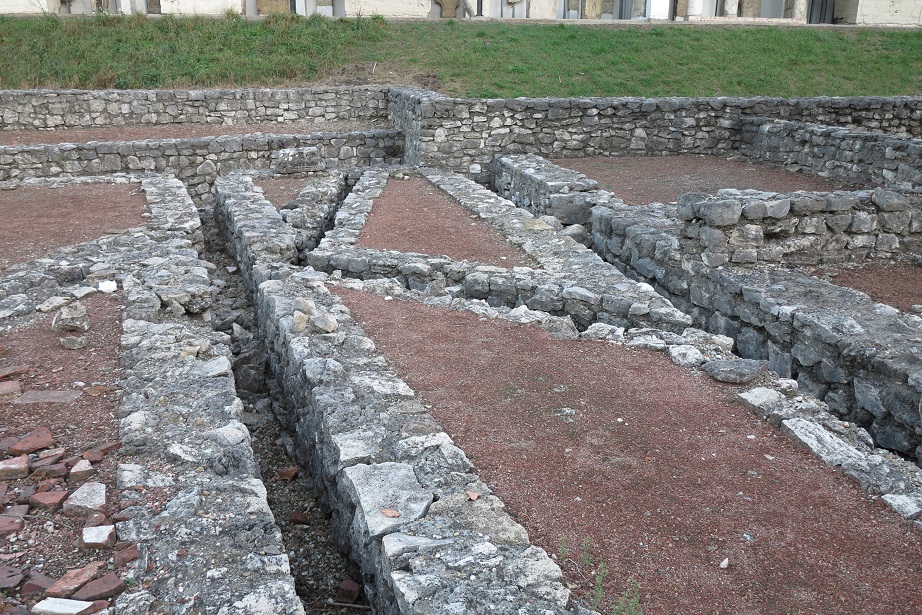
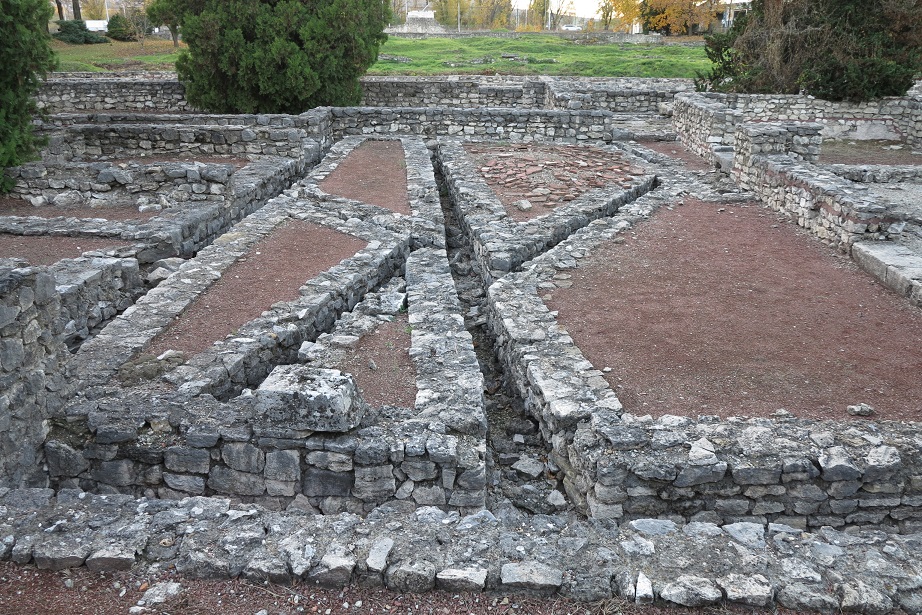
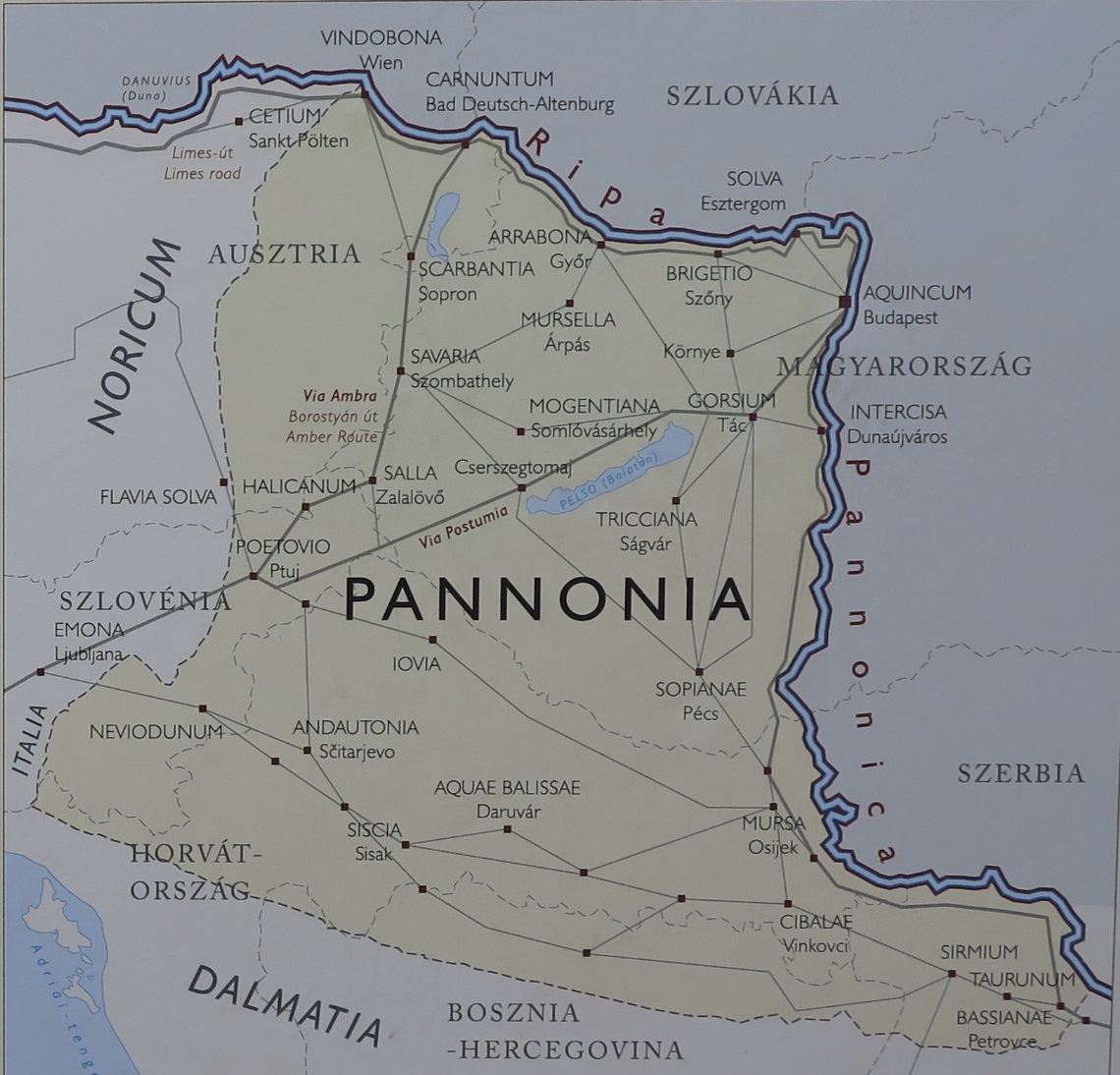
Aquincum egy római katonai tábor és polgári település volt a mai Budapest (óbudai) területén. A középkor történetírói Aquincum romjait, a mondai város Szikambria (Sicambre, Sicamber, Syccamber, Skambria, Skanboria) romjainak vélték. A rómaiak az első század második felében foglalták el a Dunántúlt. Budapest területének írásos történelme a római helyőrséggel, Aquincummal kezdődik, amelyet 89 körül alapítottak a Duna jobb partján, egy kelta település közelében. Aquincum 106-tól a 4. század végéig Alsó-Pannónia központja volt. Virágkora a 2–3. századra esett. 1778-ban egy óbudai sváb szőlősgazda római padlófűtés (hypocaustum) maradványaira talált munka közben. A leletet Schönvisner István azonosította Aquincum városával. A II. világháború utáni helyreállítási munkák és a folyamatos korszerűsítések óriási földmunkái folytán sorra kerülnek elő a föld alól az ókori emlékek, ezért a kétezer éves Aquincum nemcsak a jelenlegi romterület, hanem a teljes budai oldal és a pesti belváros területe is.
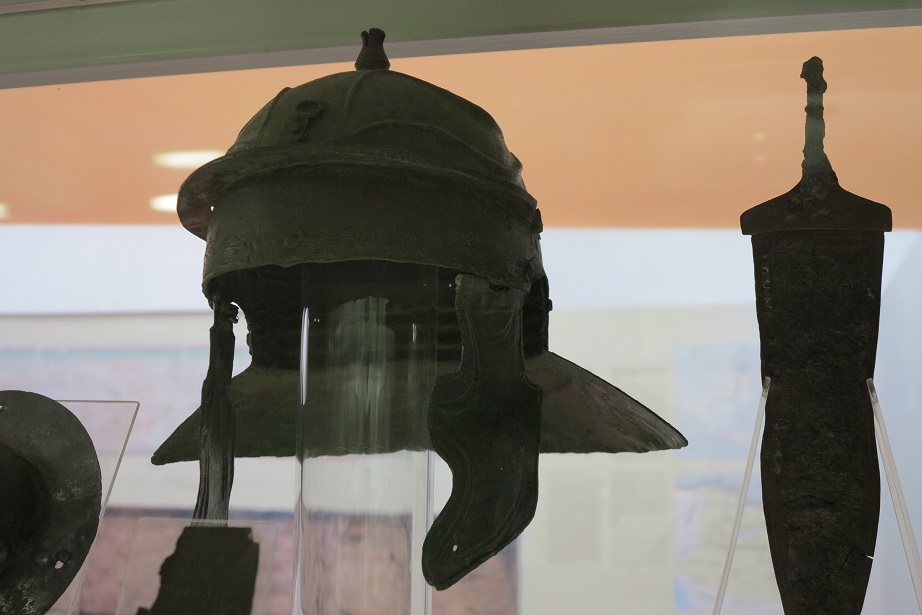
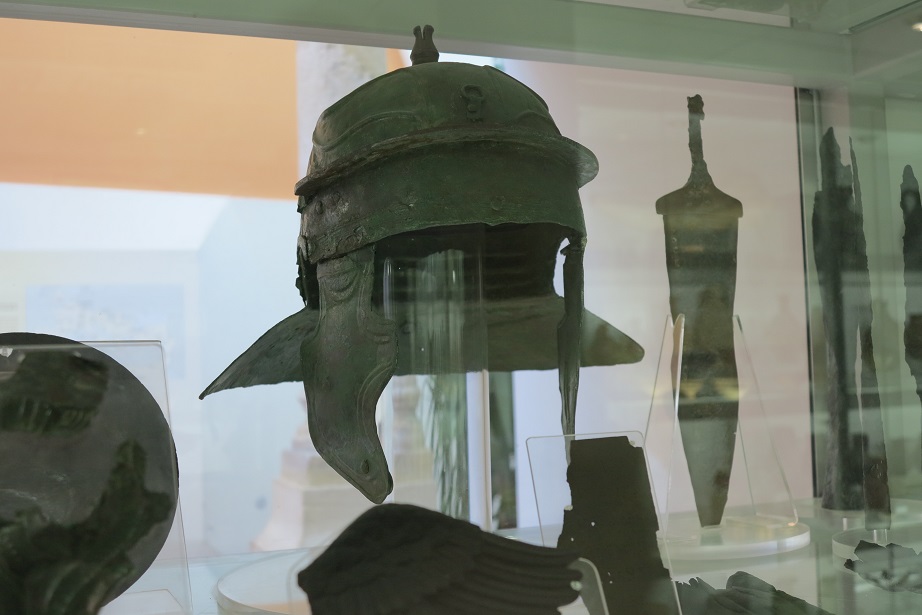
Was an ancient city, situated on the northeastern borders of the province of Pannonia within the Roman Empire. The ruins of the city can be found today in Budapest. It is believed that Marcus Aurelius wrote at least part of his book Meditations at Aquincum. Aquincum was originally settled by the Eravisci, a Celtic tribe. Aquincum served as a military base (castrum), having been part of the Roman border protection system called limes. Around AD 41-54, a 500-strong cavalry unit arrived, and a Roman legion of 6,000 men (Legio II Adiutrix) was stationed here by AD 89. The city gradually grew around the fortress, and after Pannonia was reorganised by the Romans in AD 106, Aquincum became the capital city of the Roman province of Pannonia Inferior, holding that position until the administrative reform of Diocletian, more than a hundred years later. Under Hadrian, the city obtained municipal status, while under Septimius Sever, Aquincum became a colonia.
Being the centre of operations on the Roman frontier against the neighbouring Iazyges, Aquincum was occasionally the headquarters of emporers.
The city had around 30,000 to 40,000 inhabitants by the end of the 2nd century, and covered a significant part of the area today known as the Óbuda district within Budapest. Ruins from the old Roman settlement can be seen in other parts of Budapest as well, notably Contra-Aquincum. These Roman structures were, during the 2nd and 3rd century AD, the heart of the commercial life of the Pannonia province. The excavations show evidence of the lifestyle of this period. The most important monuments in Aquincum are the two amphitheatres: the Aquincum Civil Amphitheatre and the Aquincum Military Amphitheatre, built in the 1st century AD.
CONTRA AQUINCUM HERE!
CIVIL AMPHITEATRE HERE!
MILITARY AMPHITEATRE HERE!